Full Stack AI Agents using NextJS and LangGraph
Learn how to build full stack AI agents using NextJS and LangGraph deployed on AWS and Vercel (with source code)
Most tutorials about building AI agents focus solely on the backend implementation or provide simplified examples. In this post, we'll explore how to build production-ready full stack AI agents using LangGraph and NextJS, drawing from two real-world example projects:
You can play with the example agents on the APSquared AI Tools page.
Introduction
Building production-ready AI agents requires more than just prompt engineering. You need a full stack approach that combines agent logic with user interfaces and persistence. This post explores an architecture using LangGraph for agent orchestration and NextJS for the frontend.
Why Full Stack Agents?
While many tutorials demonstrate how to build AI agents using frameworks like LangChain or LangGraph, they often miss crucial aspects of production applications:
- User Interface - How users interact with the agent
- State Management - How to track and update agent progress
- Asynchronous Processing - Handling long-running agent tasks
- Error Handling - Gracefully managing failures
- Result Persistence - Saving and retrieving agent results
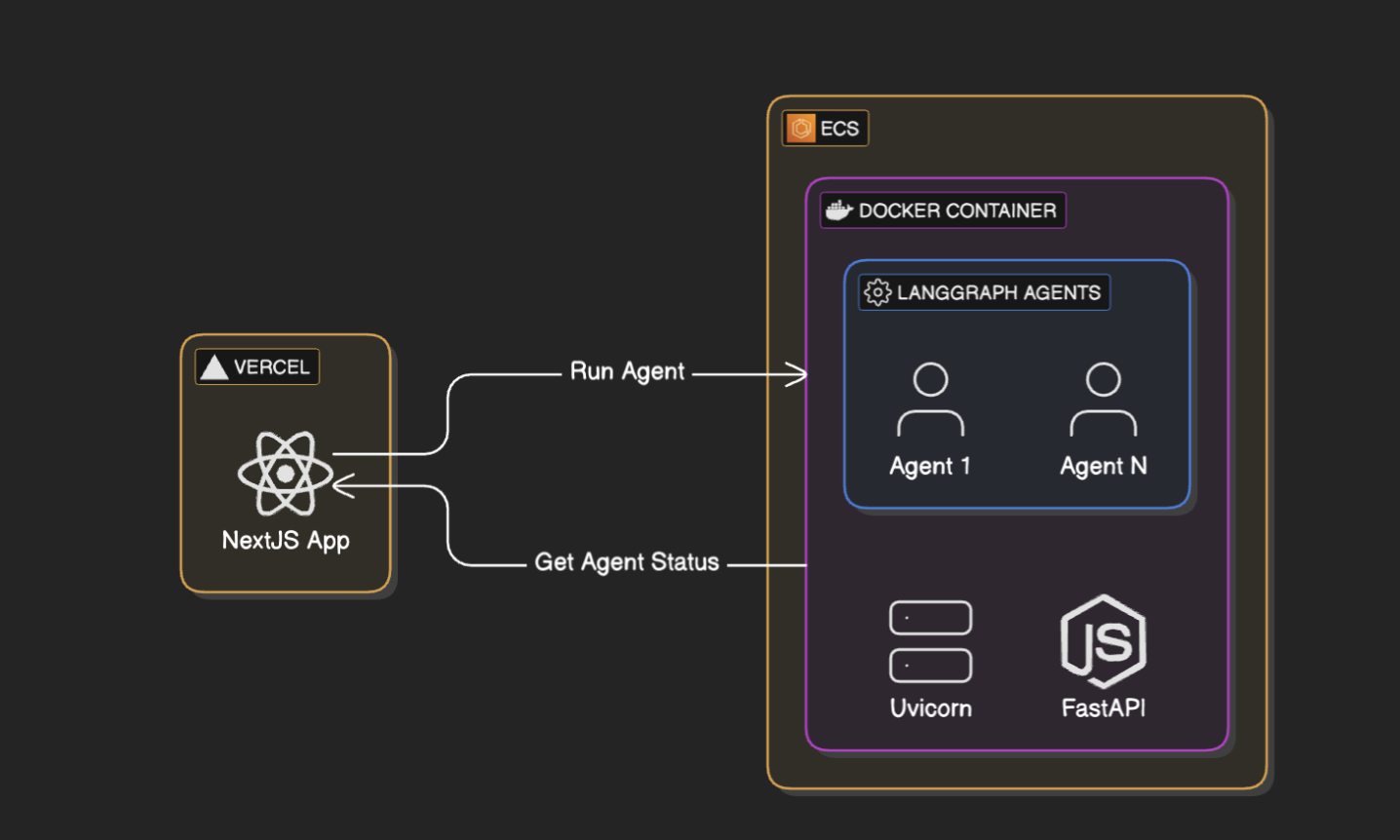
Architecture Overview
The solution consists of two main components:
Backend (LangGraph Agents)
The backend service implements the actual agent logic using LangGraph. Each agent is defined as a state machine with:
- Clear input/output types
- State management
- Progress tracking
- Error handling
- Asynchronous execution
Frontend (NextJS Application)
The frontend provides:
- Clean user interface for agent interaction
- Real-time status updates
- Result visualization
- Error handling
- Shareable results via URLs
Implementation Details
Backend Agent Structure
Each agent follows a consistent pattern:
- Define Types:
export interface AgentInput {
// Input parameters
}
export interface AgentState extends BaseState {
// Agent-specific state
results?: any[];
status?: string;
}
- Create Agent Client:
export class AgentClient extends BaseAgentClient {
constructor() {
super(AGENT_NAME);
}
async startAgent(input: AgentInput): Promise<AgentState> {
const response = await this.startAgent(input);
return response as AgentState;
}
async getStatus(runId: string): Promise<AgentState> {
const response = await this.getStatus(runId);
return response as AgentState;
}
}
Frontend Implementation
The frontend uses a reusable pattern for all agents:
- API Routes:
// start/route.ts
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const body = await request.json();
try {
const response = await agentClient.startAgent(body);
return NextResponse.json(response);
} catch (error) {
return NextResponse.json({ error: 'Failed to start agent' }, { status: 500 });
}
}
// status/[runId]/route.ts
export async function GET(
request: Request,
{ params }: { params: { runId: string } }
) {
try {
const response = await agentClient.getStatus(params.runId);
return NextResponse.json(response);
} catch (error) {
return NextResponse.json({ error: 'Failed to get status' }, { status: 500 });
}
}
- Reusable Agent Page Component:
export default function AgentPage<T extends AgentState>({
agentName,
agentDisplayName,
sampleSearches,
formFields,
children: {
renderResults,
renderLoadingState
}
}: AgentPageProps<T>) {
// State management
const [runId, setRunId] = useState<string | null>(null);
const [agentState, setAgentState] = useState<T | null>(null);
// Status polling
useEffect(() => {
if (runId) {
const pollInterval = setInterval(async () => {
const response = await fetch(`/api/${agentName}/status/${runId}`);
const data = await response.json();
setAgentState(data);
if (data.status !== "running") {
clearInterval(pollInterval);
}
}, 10000);
return () => clearInterval(pollInterval);
}
}, [runId]);
// ... form handling and rendering
}
Key Features
- Asynchronous Execution: Agents run asynchronously with progress updates
- State Management: Clear state transitions and progress tracking
- Error Handling: Graceful error handling at all levels
- Result Persistence: Results accessible via unique URLs
- Reusable Components: Common patterns extracted into reusable components
- Type Safety: Full TypeScript support throughout the stack
Example Agents
Check out our example agents:
- College Finder Agent - Helps find colleges based on criteria
- Team Roster Agent - Generates optimized sports team rosters
- Marketing Agent - Creates marketing plans for SaaS products
Each agent demonstrates different aspects of the framework while following the same architectural patterns.
Getting Started
To create your own agent:
- Define your agent types (input/state)
- Implement the agent logic using LangGraph
- Create an agent client extending BaseAgentClient
- Add API routes for start/status
- Create a frontend page using the AgentPage component
- Implement result rendering logic
Conclusion
Building full stack AI agents requires more than just the agent logic. This architecture provides a solid foundation for production-ready applications with:
- Clean separation of concerns
- Reusable patterns
- Type safety
- Error handling
- User-friendly interfaces
The example repositories demonstrate these patterns in action with real-world agents.
Check out the repositories for complete examples:
Connect With Us
Have questions or want to discuss AI agents? Connect with us on social media:
- X (Twitter): @APSquaredDev
- BlueSky: @apsquared.bsky.social
We're always happy to chat about AI development, answer questions, and share insights about building full stack AI agents!